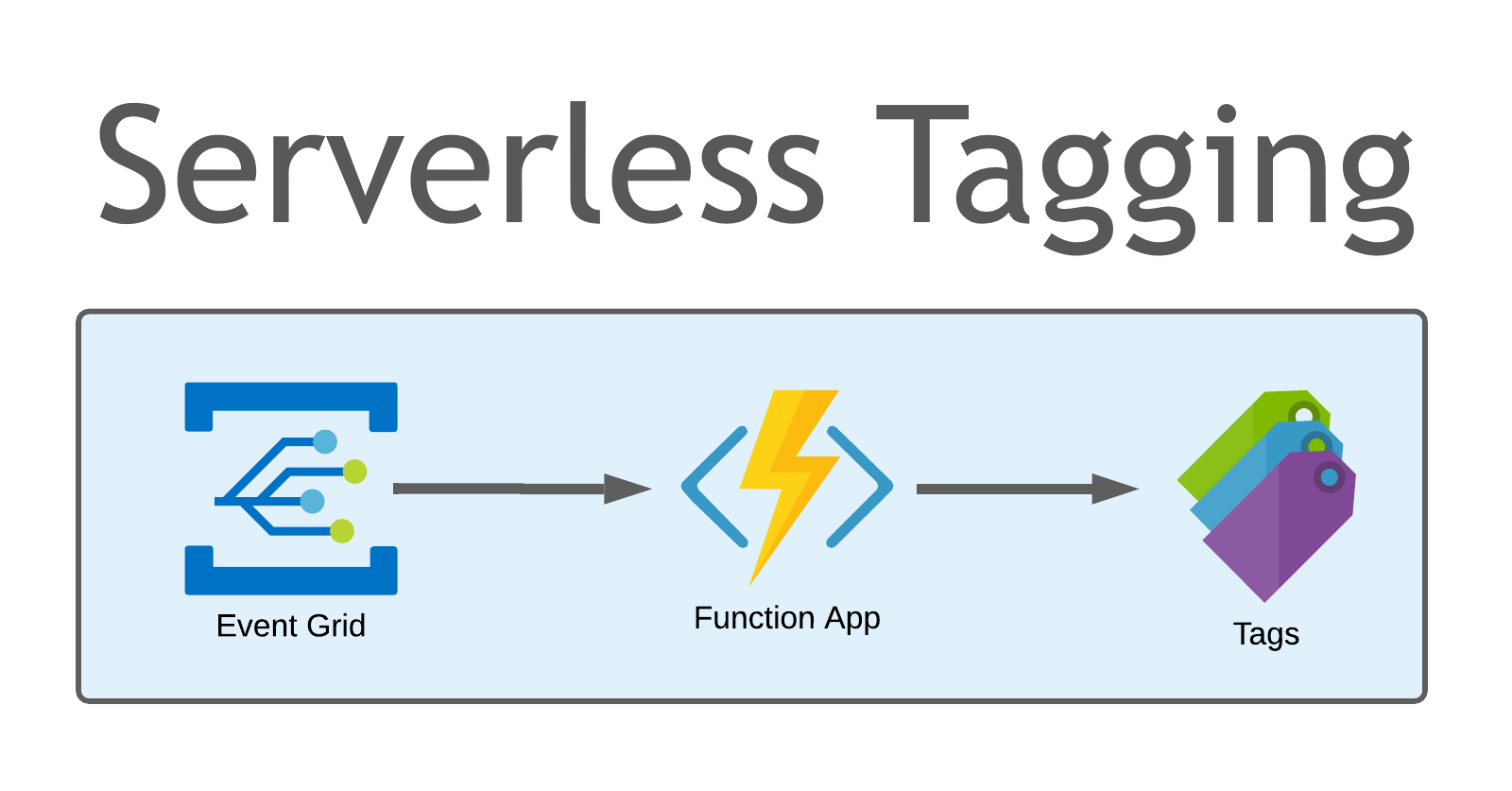
Azure AutoTagger is a lightweight, low-cost serverless solution that can easily be deployed to an Azure subscription. Once deployed Azure AutoTagger monitors for ResourceWriteSucess events within the subscription and triggers an Azure Function to automatically apply a LastModifiedTimestamp and LastModifiedBy tag. Any organization should develop and implement it’s own tagging strategy (Azure’s Cloud Adoption Framework is a great start). This solution can be a complimentary piece to a more comprehensive tagging strategy, and can be useful when deployed to test/development/sandbox subscriptions where resources sometimes have a habit of sticking around longer than they were intended.
https://github.com/acampb/AzureAutoTagger: Contains the ARM template code to deploy the infrastructure and role assignments to the subscription
https://github.com/acampb/AzureAutoTaggerFunction: Contains the Azure Function PowerShell code
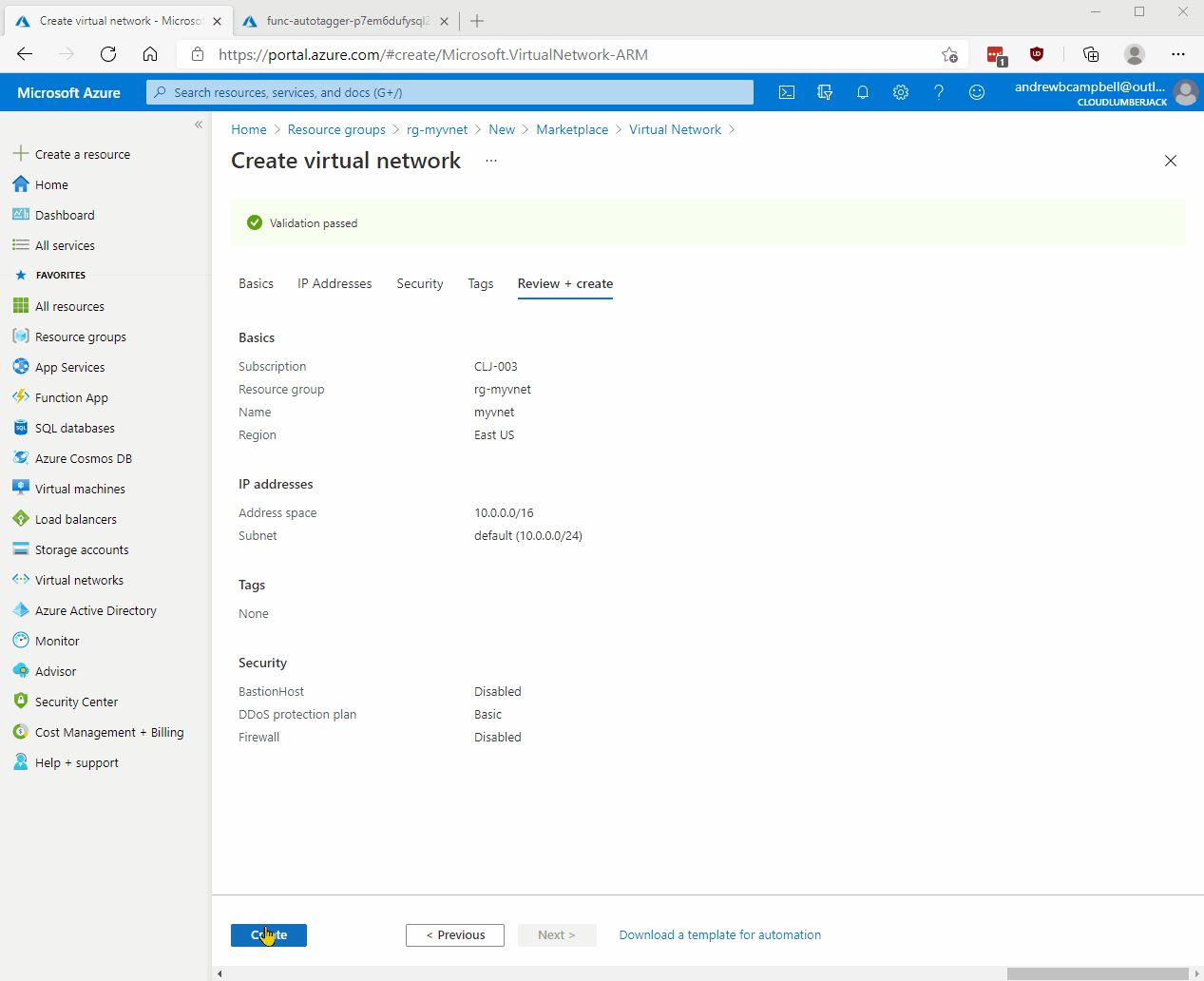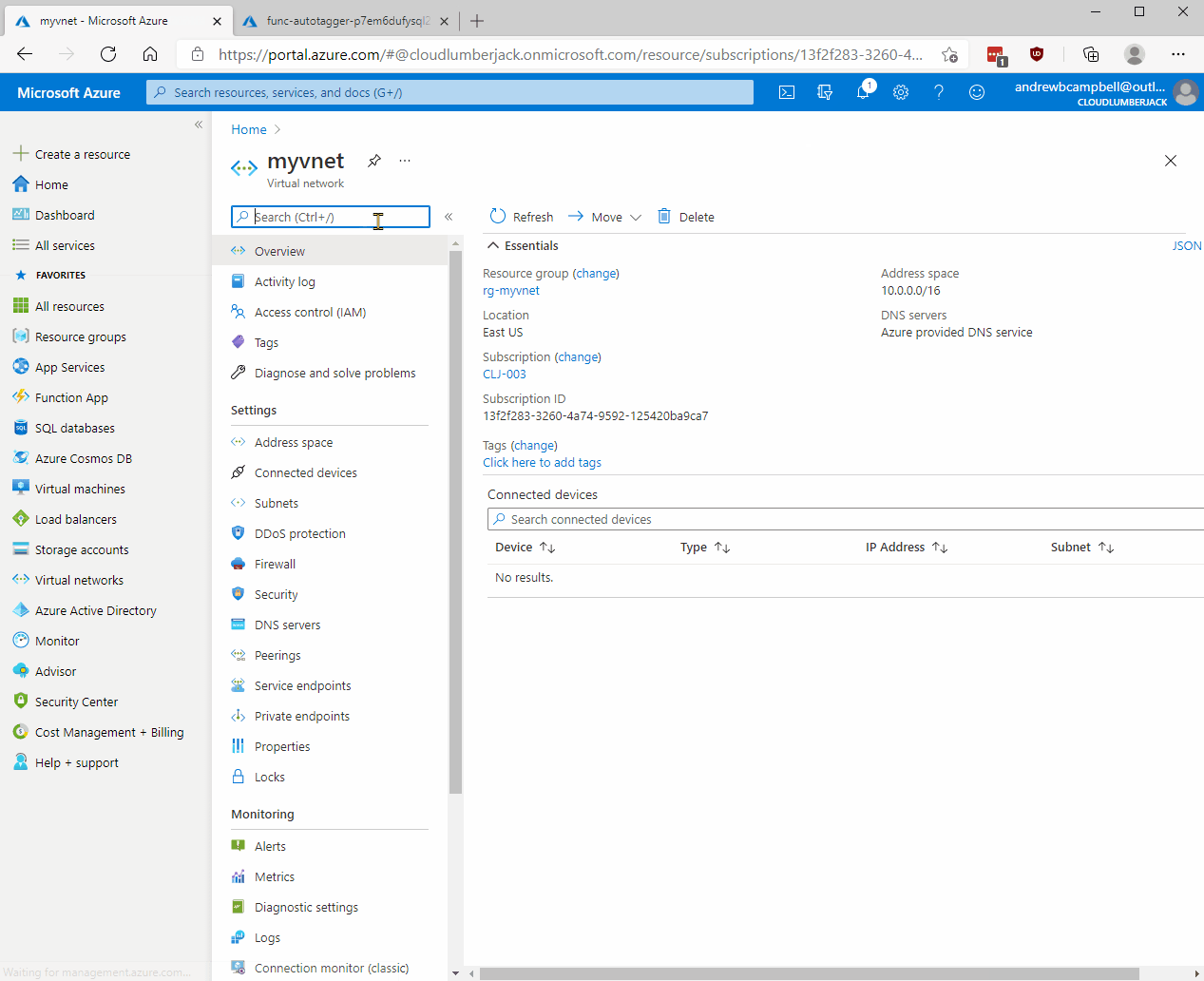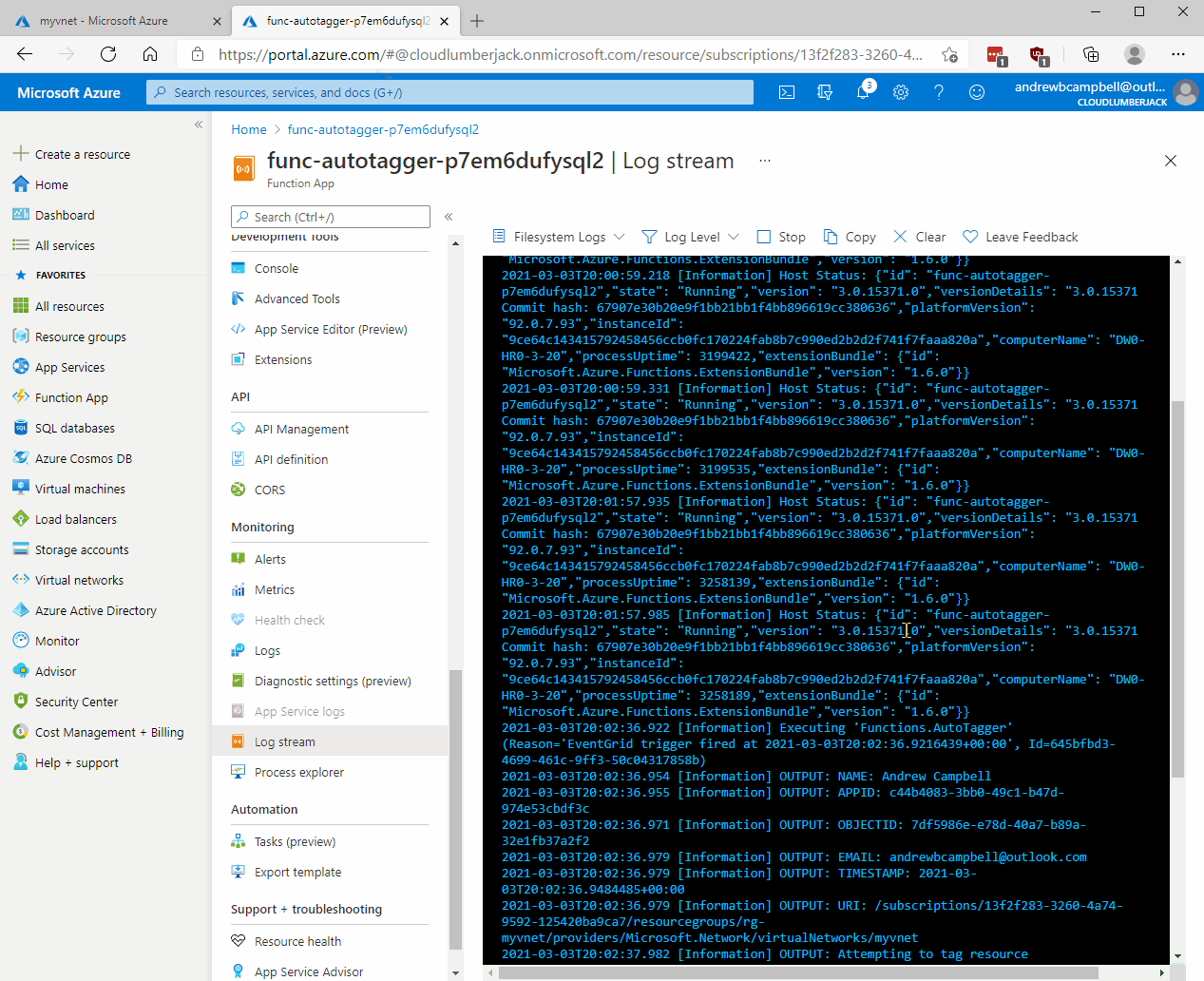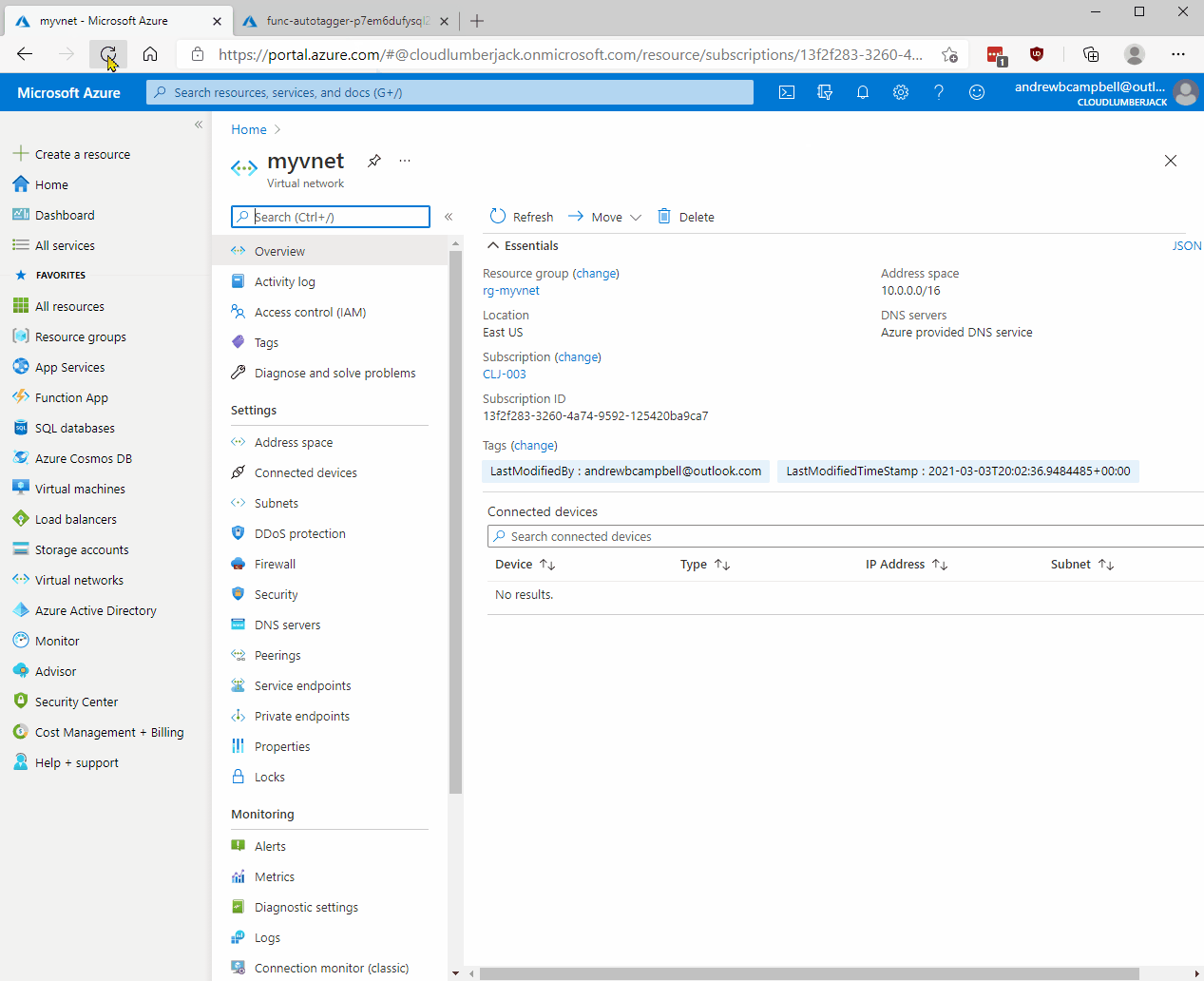
Deployment
Important: You must have Owner permissions on the subscription you intend to deploy this to. The template will create a managed identity and assign it to the
ReaderandTag Contributorroles.
Use the Deploy to Azure button to easily deploy this solution in a subscription
– OR –
- Clone the GitHub repo locally
git clone https://github.com/acampb/AzureAutoTagger.git
- Initiate an ARM Template deployment with Azure PowerShell or Azure CLI
Azure PowerShell:
New-AzDeployment -Location "East US" -TemplateFile ".\azuredeploy.json" -resourceGroupName "rg-autotagger" -Verbose
Azure CLI:
az deployment create --location "West US" --template-file ".\azuredeploy.json" --parameters resourceGroupName=rg-autotagger
Event Grid
Azure Event Grid allows you to build applications with event-based architectures. Configure the Azure resource you would like to subscribe to, and then give the event handler or WebHook endpoint to send the event to. Event Grid has built-in support for events coming from Azure services, like storage blobs, resource groups, and subscriptions. Event Grid also has support for your own events, using custom topics.
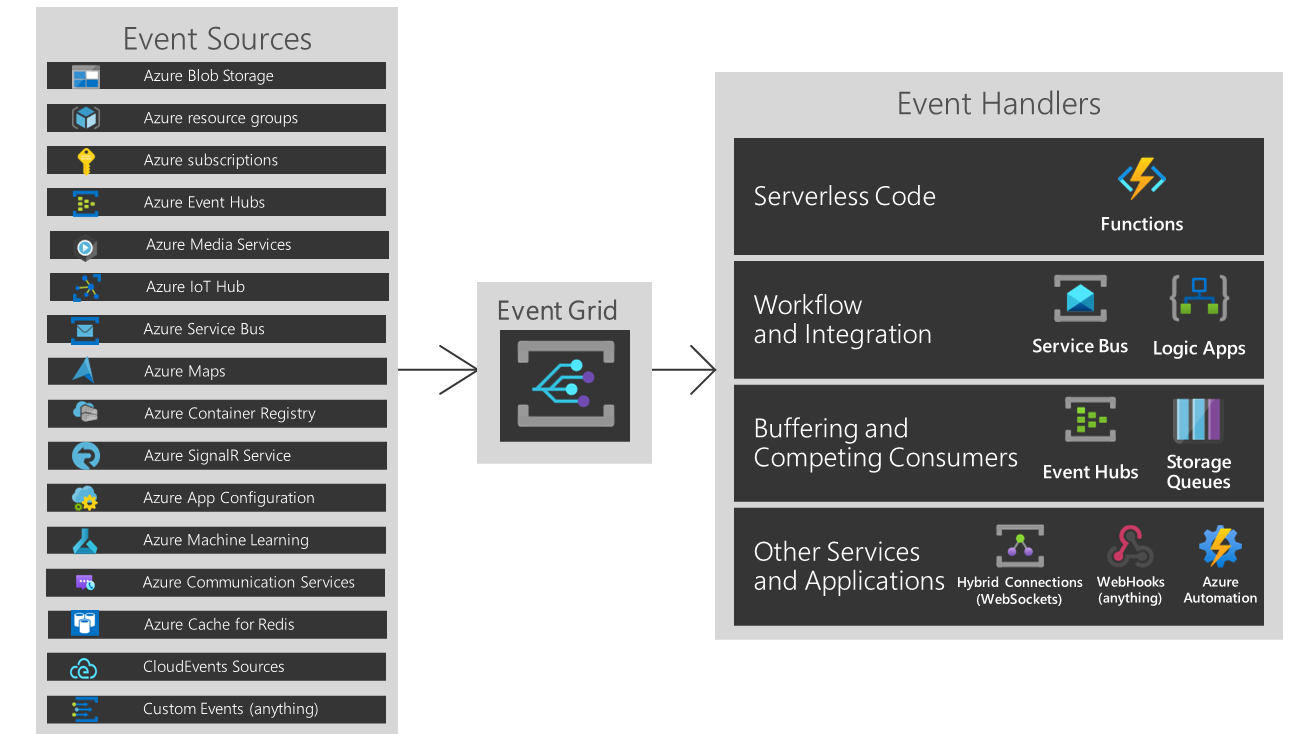
There are five concepts in Azure Event Grid that let you get going:
- Events - JSON data describing what happened.
- Event Sources - Azure service the event took place (or custom). In this solution this is the Azure Subscription itself.
- Topics - The deployed Azure resource (endpoint) where publishers send events.
- Event subscriptions - The endpoint or built-in mechanism to route events, sometimes to more than one handler. Subscriptions are also used by handlers to intelligently filter incoming events.
- Event handlers - The app or service reacting to the event. In this solution we are using an Azure Function App
The Azure AutoTagger solution starts by creating an Event Grid System Topic configured with the Azure subscription as the event source. An Event Subscription is then configured to consume the events emitted by the Azure subscription. The Event Subscription only routes events of the type ResourceWriteSuccess, so we are only sending events to this subscription when a resource is written (created or changed). The Event Subscription is connected to the Azure Function App as it’s Event Handler.
The events emitted by the Azure Subscription are standard JSON payloads describing what resource was changed, and the authentication claim of the identity initiating performing the resource write operation. Below is a sample event JSON from the Azure documentation:
[{
"subject": "/subscriptions/{subscription-id}/resourcegroups/{resource-group}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{storage-name}",
"eventType": "Microsoft.Resources.ResourceWriteSuccess",
"eventTime": "2018-07-19T18:38:04.6117357Z",
"id": "4db48cba-50a2-455a-93b4-de41a3b5b7f6",
"data": {
"authorization": {
"scope": "/subscriptions/{subscription-id}/resourcegroups/{resource-group}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{storage-name}",
"action": "Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/write",
"evidence": {
"role": "Subscription Admin"
}
},
"claims": {
"aud": "{audience-claim}",
"iss": "{issuer-claim}",
"iat": "{issued-at-claim}",
"nbf": "{not-before-claim}",
"exp": "{expiration-claim}",
"_claim_names": "{\"groups\":\"src1\"}",
"_claim_sources": "{\"src1\":{\"endpoint\":\"{URI}\"}}",
"http://schemas.microsoft.com/claims/authnclassreference": "1",
"aio": "{token}",
"http://schemas.microsoft.com/claims/authnmethodsreferences": "rsa,mfa",
"appid": "{ID}",
"appidacr": "2",
"http://schemas.microsoft.com/2012/01/devicecontext/claims/identifier": "{ID}",
"e_exp": "{expiration}",
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/surname": "{last-name}",
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/givenname": "{first-name}",
"ipaddr": "{IP-address}",
"name": "{full-name}",
"http://schemas.microsoft.com/identity/claims/objectidentifier": "{ID}",
"onprem_sid": "{ID}",
"puid": "{ID}",
"http://schemas.microsoft.com/identity/claims/scope": "user_impersonation",
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/nameidentifier": "{ID}",
"http://schemas.microsoft.com/identity/claims/tenantid": "{ID}",
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/name": "{user-name}",
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/upn": "{user-name}",
"uti": "{ID}",
"ver": "1.0"
},
"correlationId": "{ID}",
"resourceProvider": "Microsoft.Storage",
"resourceUri": "/subscriptions/{subscription-id}/resourcegroups/{resource-group}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{storage-name}",
"operationName": "Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/write",
"status": "Succeeded",
"subscriptionId": "{subscription-id}",
"tenantId": "{tenant-id}"
},
"dataVersion": "2",
"metadataVersion": "1",
"topic": "/subscriptions/{subscription-id}"
}]
The event JSON contains some interesting data that we will utilize later within our Azure function, notably the ResourceUri and some claim information about the user or service principal performing the operation. The Event Subscription is configured to trigger our Azure Function to execute on a new event and will pass this JSON data object to the Function as a parameter in our PowerShell script.
You may be thinking “wait, wont the Azure Function writing tags create an endless loop of insanity?”. Yes, yes it will, unless we configure some additional filtering. Within the Event Grid Subscription configure we also create an advanced filter to exclude the event if the $data.claims.appid matches the appid of the Azure Function’s identity.
Azure Function
Azure Functions is a serverless solution that allows you to write less code, maintain less infrastructure, and save on costs. Instead of worrying about deploying and maintaining servers, the cloud infrastructure provides all the up-to-date resources needed to keep your applications running.
A PowerShell Azure Function is represented as a PowerShell script that executes when triggered. Each function script has a related function.json file that defines how the function behaves, such as how it’s triggered and its input and output parameters.
PowerShell Functions take in parameters that match the names of all the input bindings defined in the function.json file. A TriggerMetadata parameter is also passed that contains additional information on the trigger that started the function.
The Azure AutoTagger solution deploys a Function App containing a single PowerShell script Function named AutoTagger. The AutoTagger Function executes a PowerShell script which parses the JSON data provided from the Event Grid for which user or service principal modified the Azure resource, and what Resource Uri was modified. The script then creates a hashtable and updates the tags on the resource. The code performs an Update-AzTag -Merge operation so any existing tags are preserved.
param($eventGridEvent, $TriggerMetadata)
# Make sure to pass hashtables to Out-String so they're logged correctly
#$eventGridEvent | Out-String | Write-Host
# uncomment for claims detail for debugging
#Write-Output $eventGridEvent.data.claims | Format-List
$name = $eventGridEvent.data.claims.name
Write-Output "NAME: $name"
$appid = $eventGridEvent.data.claims.appid
Write-Output "APPID: $appid"
$email = $eventGridEvent.data.claims.'http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/emailaddress'
Write-Output "EMAIL: $email"
$time = Get-Date -Format o
Write-Output "TIMESTAMP: $time"
$uri = $eventGridEvent.data.resourceUri
Write-Output "URI: $uri"
try {
$resource = Get-AzResource -ResourceId $uri -ErrorAction Stop
If (($resource) -and
($resource.ResourceId -notlike '*Microsoft.Resources/deployments*')) {
Write-Output 'Attempting to tag resource'
If ($email) {
$lastModifiedBy = $email
} else {
$lastModifiedBy = $appid
}
$tags = @{
"LastModifiedBy" = $lastModifiedBy
"LastModifiedTimeStamp" = $time
}
try {
Update-AzTag -ResourceId $uri -Tag $tags -Operation Merge
}
catch {
Write-Output "Encountered error writing tag, may be a resource that does not support tags."
}
}
else {
Write-Output 'Excluded resource type'
}
}
catch {
Write-Output "Not able query the resource Uri. This could be due to a permissions problem (identity needs reader); or not a resource we can query"
}
Azure Resources Deployed
The entire solution consists of the six resources (pictured below) deployed to the Resource Group, and two Azure Role Assignments.
All of the resources are suffixed using the ARM template function uniqueString derived from the Azure Subscription id. This is to avoid naming conflicts on the resources which require global uniqueness.
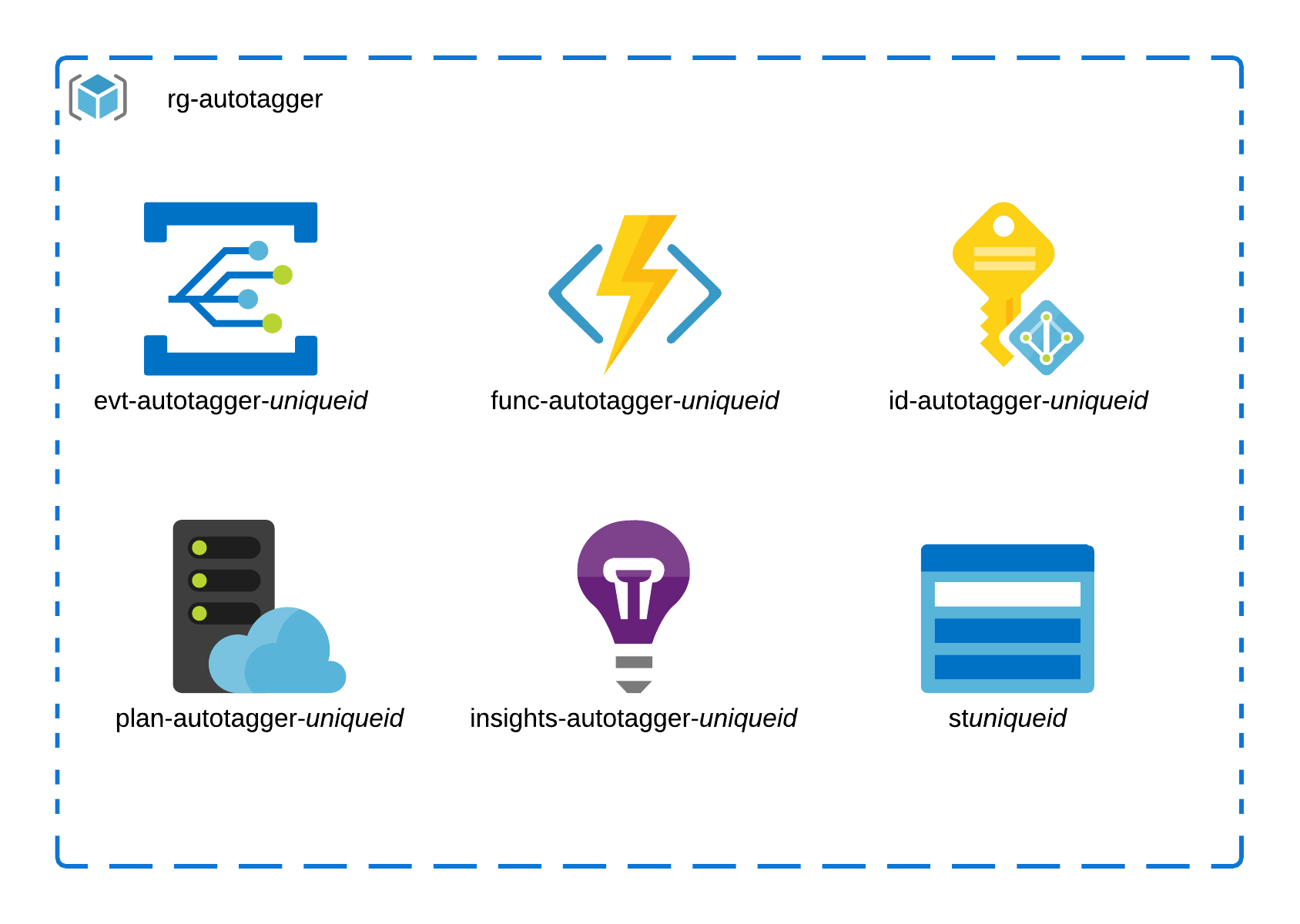
The Event Grid and Function App are the core components of the solution, the additional resources are deployed in support of the Azure Function:
- Storage Account: A storage account is required for Azure Functions to operate.
- App Service Plan: The App Service Plan is the hosting plan for the Azure Function. The plan provides the compute and memory for the function, and controls additional functionality. The deployment template defaults to the
Consumptionplan for the lowest possible cost, but this could be upgraded later if required. - Application Insights: Application Insights is deployed and configured in order to provide troubleshooting and log streaming capabilities.
- User Assigned Managed Identity: A User assigned managed identity is created and assigned to the Azure Function. When the Function’s PowerShell code is executed it is authenticated to the Azure subscription using this identity. This managed identity is also assigned to the
ReaderandTag ContributorRBAC roles.
ARM Template Deployment
This ARM Template performs a subscription level deployment. It will initiate several linked deployments to deploy and configure all of the resources required in the solution.
Create a new Resource Group with the name specified in the parameter
resourceGroupName. Defaults torg-autotaggerif no other value is specifiedPerform a linked template deployment to create the Event Grid and Function App resources. Uses https://github.com/acampb/AzureAutoTagger/blob/main/eventgridfunction.json
Create the User Assigned Managed Identity
Create the App Service plan
Create the Storage Account
Create the Function App
Configure the Function App source control to deploy the PowerShell function from the application repo: https://github.com/acampb/AzureAutoTaggerFunction
Create the Event Grid System Topic using the subscription as a source
Create the Event Grid Subscription, configured to include only
ResourceWriteSuccessevents, and an advanced filter to exclude events from the Managed Identity App IdCreate the Application Insights
Output the Managed Identity Principal Id
Perform a linked template deployment to assign the Managed Identity to the
Readerrole. Uses https://github.com/acampb/AzureAutoTagger/blob/main/rbac.jsonPerform a linked template deployment to assign the Managed Identity to the
Tag Contributorrole. Uses https://github.com/acampb/AzureAutoTagger/blob/main/rbac.json